Misinformation About Fentanyl Threatens To Undermine Overdose Response
/By Henry Larweh, KFF Health News
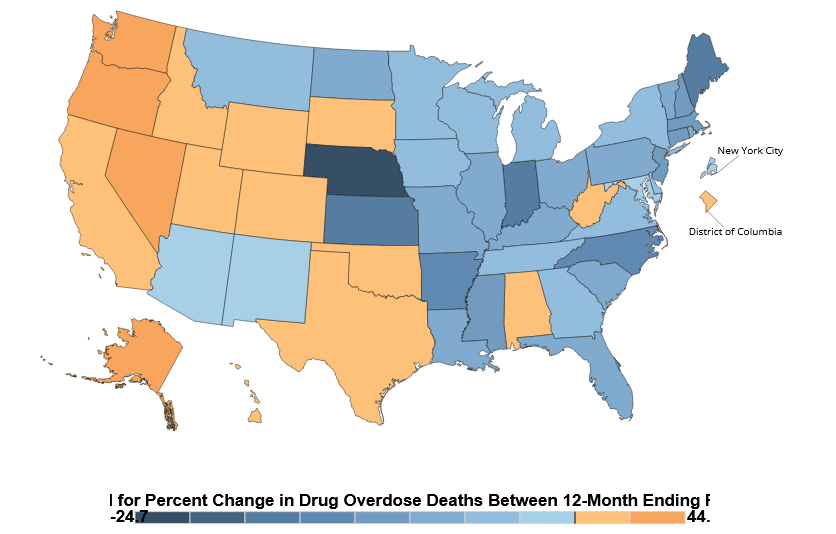
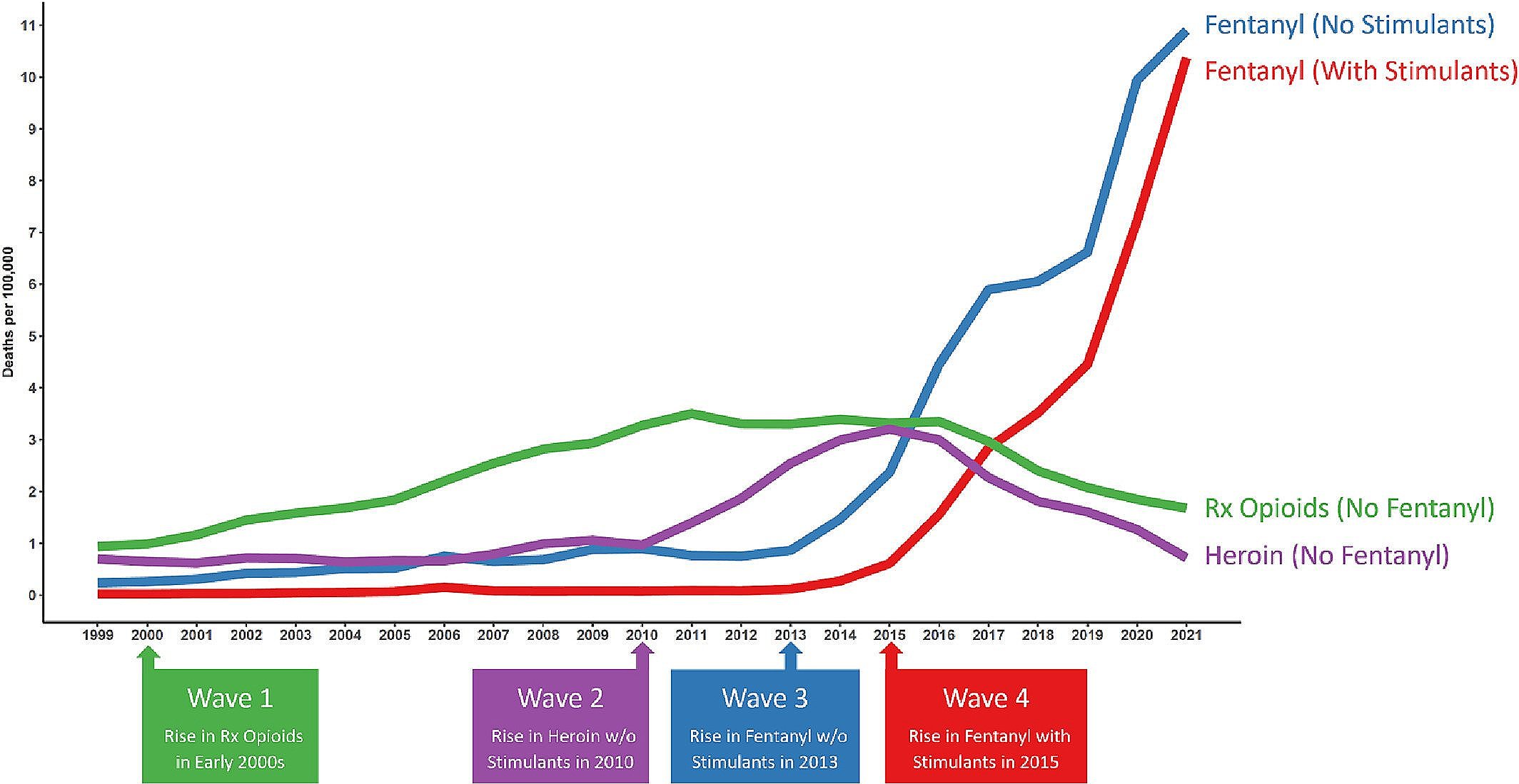
Fentanyl, the deadly synthetic opioid driving the nation’s high drug overdose rates, is also caught up in another increasingly serious problem: misinformation.
False and misleading narratives on social media, in news reports, and even in popular television dramas suggesting people can overdose from touching fentanyl — rather than ingesting it — are now informing policy and spending decisions.
In an episode of the CBS cop drama “Blue Bloods,” for instance, Detective Maria Baez becomes comatose after accidentally touching powdered fentanyl. In another drama, “S.W.A.T.,” Sgt. Daniel “Hondo” Harrelson warns his co-workers: “You touch the pure stuff without wearing gloves, say good night.”
While fentanyl-related deaths have drastically risen over the past decade, no evidence suggests any resulted from incidentally touching or inhaling it, and little to no evidence that any resulted from consuming it in marijuana products. (Recent data indicates that fentanyl-related deaths have begun to drop.)
There is also almost no evidence that law enforcement personnel are at heightened risk of accidental overdoses due to such exposures. Still, there is a steady stream of reports — which generally turn out to be false — of officers allegedly becoming ill after handling fentanyl.
“It’s only in the TV dramas” where that happens, said Brandon del Pozo, a retired Burlington, Vermont, police chief who researches policing and public health policies and practices at Brown University.
In fact, fentanyl overdoses are commonly caused by ingesting the drug illicitly as a pill or powder. And most accidental exposures occur when people who use drugs, even those who do not use opioids, unknowingly consume fentanyl because it is so often used to “cut” street drugs such as heroin and cocaine.
Despite what scientific evidence suggests about fentanyl and its risks, misinformation can persist in public discourse and among first responders on the front lines of the crisis. Daniel Meloy, a senior community engagement specialist at the drug recovery organizations Operation 2 Save Lives and QRT National, said he thinks of misinformation as “more of an unknown than it is an anxiety or a fear.”
“We’re experiencing it often before the information” can be understood and shared by public health and addiction medicine practitioners, Meloy said.
Some state and local governments are investing money from their share of the billions in opioid settlement funds in efforts to protect first responders from purported risks perpetuated through fentanyl misinformation.
In 2022 and 2023, 19 cities, towns, and counties across eight states used settlement funds to purchase drug detection devices for law enforcement agencies, spending just over $1 million altogether. Two mass spectrometers were purchased for at least $136,000 for the Greeley, Colorado, police department, “to protect those who are tasked with handling those substances.”
Del Pozo, the retired police chief, said fentanyl is present in most illicit opioids found at the scene of an arrest. But that “doesn’t mean you need to spend a lot of money on fentanyl detection for officer safety,” he said. If that spending decision is motivated by officer safety concerns, then it’s “misspent money,” del Pozo said.
Fentanyl misinformation is affecting policy in other ways, too.
Florida, for instance, has on the books a law that makes it a second-degree felony to cause an overdose or bodily injury to a first responder through this kind of secondhand fentanyl exposure. Similar legislation has been considered by states such as Tennessee and West Virginia, the latter stipulating a penalty of 15 years to life imprisonment if the exposure results in death.
Public health advocates worry these laws will make people shy away from seeking help for people who are overdosing.
“A lot of people leave overdose scenes because they don’t want to interact with police,” said Erin Russell, a principal with Health Management Associates, a health care industry research and consulting firm. Florida does include a caveat in its statute that any person “acting in good faith” to seek medical assistance for someone they believe to be overdosing “may not” be arrested, charged, or prosecuted.
‘You Can Get It Through Your Fingers’
And even when public policy is crafted to protect first responders as well as regular people, misinformation can undermine a program’s messaging.
Take Mississippi’s One Pill Can Kill initiative. Led by the state attorney general, Lynn Fitch, the initiative aims to provide resources and education to Mississippi residents about fentanyl and its risks.
While it promotes the availability and use of harm reduction tools, such as naloxone and fentanyl test strips, Fitch has also propped up misinformation.
At the 2024 Mississippi Coalition of Bail Sureties conference, Fitch said, “If you figure out that pill’s got fentanyl, you better be ready to dispose of it, because you can get it through your fingers,” based on the repeatedly debunked belief that a person can overdose by simply touching fentanyl.
Officers on the ground, meanwhile, sometimes are warned to proceed with caution in providing lifesaving interventions at overdose scenes because of these alleged accidental exposure risks. This caution is often evidenced in a push to provide first responders with masks and other personal protective equipment.
Fitch told the crowd at the conference: “You can’t just go out and give CPR like you did before.”
However, as with other secondhand exposures, the risk for a fentanyl overdose from applying mouth-to-mouth is negligible, with no clinical evidence to suggest it has occurred.
Her comments underscore growing concerns, often not supported by science, that officers and first responders increasingly face exposure risks during overdose responses. Her office did not respond to questions about these comments.
Health care experts say they are not against providing first responders with protective equipment, but that fentanyl misinformation is clouding policy and risks delaying critical interventions such as CPR and rescue breathing.
“People are afraid to do rescue breathing because they’re like, ‘Well, what if there’s fentanyl in the person’s mouth,’” Russell said. Hesitating for even a moment because of fentanyl misinformation could delay a technique that “is incredibly important in an overdose response.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues.