The Horrors of TMJ: Futile Treatments for Chronic Jaw Pain
/By Brett Kelman, KFF Health News, and Anna Werner, CBS News
A TMJ patient in Maine had six surgeries to replace part or all of the joints of her jaw.
Another woman in California, desperate for relief, used a screwdriver to lengthen her jawbone daily, turning screws that protruded from her neck.
A third in New York had bone from her rib and fat from her belly grafted into her jaw joint, and twice a prosthetic eyeball was surgically inserted into the joint as a placeholder in the months it took to make metal hinges to implant into her jaw.
“I feel like Mr. Potato Head,” said Jenny Feldman, 50, of New York City, whose medical records show she’s had at least 24 TMJ-related surgeries since she was a teenager. “They’re moving ribs into my face, and eyeballs, and I feel like a toy … put together [by] somebody just tinkering around.”
These are some of the horrors of temporomandibular joint disorders, known as TMJ or TMD, which afflict up to 33 million Americans, according to the National Institutes of Health.
Dentists have attempted to heal TMJ patients for close to a century, and yet the disorders remain misunderstood, under-researched, and ineffectively treated, according to an investigation by KFF Health News and CBS News.
JENNY FELDMAN
Dental care for TMJ can do patients more harm than good, and a few fall into a spiral of futile surgeries that may culminate in their jaw joints being replaced with metal hinges, according to medical and dental experts, patients, and their advocates speaking in interviews and video testimony submitted to the FDA.
TMJ disorders cause pain and stiffness in the jaw and face that can range from discomfort to disabling, with severe symptoms far more common in women. Dentists have commonly treated the disorder with splints and orthodontics. And yet these treatments are based on “strongly held beliefs” and “inadequate research” — not compelling scientific evidence nor consistent results — according to the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine, which reviewed decades of research on the topic. The NIH echoes this message, warning that there is “not a lot of evidence” that splints reduce pain and recommends “staying away” from any treatment that permanently changes the teeth, bite, or jaw.
“I would say that the treatments overall have not been effective, and I can understand why,” said Rena D’Souza, director of the NIH’s National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. “We don’t understand the disease.”
For this investigation, journalists with KFF Health News and CBS News interviewed 10 TMJ patients with severe symptoms who said they felt trapped by an escalating series of treatments that began with splints or dental work and grew into multiple surgeries with diminishing returns and dwindling hope.
In every interview, the patients said the TMJ pain worsened throughout their treatment and they regretted some, if not all, of the care they received.
“The grand irony to me is that I went to the doctor for headaches and neck pain, and I’ve had 13 surgeries on my face and jaw, and I still have even worse neck pain,” said Tricia Kalinowski, 63, of Old Orchard Beach, Maine. “And I live with headaches and jaw pain every day.”
TMJ has become an umbrella term for about 30 disorders that afflict roughly 5% to 10% of Americans. Minor symptoms may not require treatment at all, and many cases resolve by themselves over time. Severe symptoms include chronic pain and may limit the ability to eat, sleep, or talk.
In a comprehensive study of TMJ disorders by the national academies, including input from more than 110 patients, experts found that most health care professionals, including dentists, have received “minimal or no training” on TMJ disorders and patients are “often harmed” by “overly aggressive” care and the lack of proven treatments.
The American Dental Association, which represents about 160,000 dentists nationwide and establishes guidelines for the profession, declined an interview request. In a written statement, ADA President Linda Edgar said that TMJ disorders are “often managed rather than cured” and that it sees “great potential” in new efforts to research more treatment options.
Terrie Cowley, a longtime TMJ patient who leads the TMJ Association, an advocacy group that has spoken with tens of thousands of patients, said she was so disillusioned with dental care for TMJ that she advises many patients to avoid treatment entirely, potentially for years.
“Almost 100 years this has been in dentistry, and look at what we have,” Cowley said. “A whole ton of people pretending they know everything, and we don’t know anything.”
‘Not Taken Seriously’
Scientific studies have found that TMJ disorders arise up to nine times as often in women, particularly those in their 20s and 30s, leading to theories that the cause may be linked to reproductive hormones. But a true understanding of TMJ disorders remains elusive.
Kyriacos Athanasiou, a biomedical engineering professor at the University of California-Irvine, said it was because TMJ disorders are more prevalent among women that they were historically dismissed as neither serious nor complex, slowing research into the cause and treatment.
The resulting dearth of knowledge, which is glaring when compared with other joints, has been “a huge disservice” to patients, Athanasiou said. In a 2021 study he co-authored, researchers found that the knee, despite being a much simpler joint, was the subject of about six times as many research papers and grants in a single year than the jaw joint.
D’Souza agreed that TMJ disorders were “not taken seriously” for decades, along with other conditions that predominantly affect women.
“That has been a bias that is really long-standing,” she said. “And it’s certainly affected the progress of research.”
Patients have felt the effect too. In interviews, female patients said they felt patronized or trivialized by male health care providers at some point in their TMJ treatment, if not throughout. Some said they felt blamed for their own pain because they were viewed as too stressed and clenching their jaw too much.
“We desperately need research to find the reasons why more women get TMJ disease,” wrote Lisa Schmidt, a TMJ Association board member, in a 2021 newsletter from the organization. “And surgeons need to stop blaming this condition on women.”
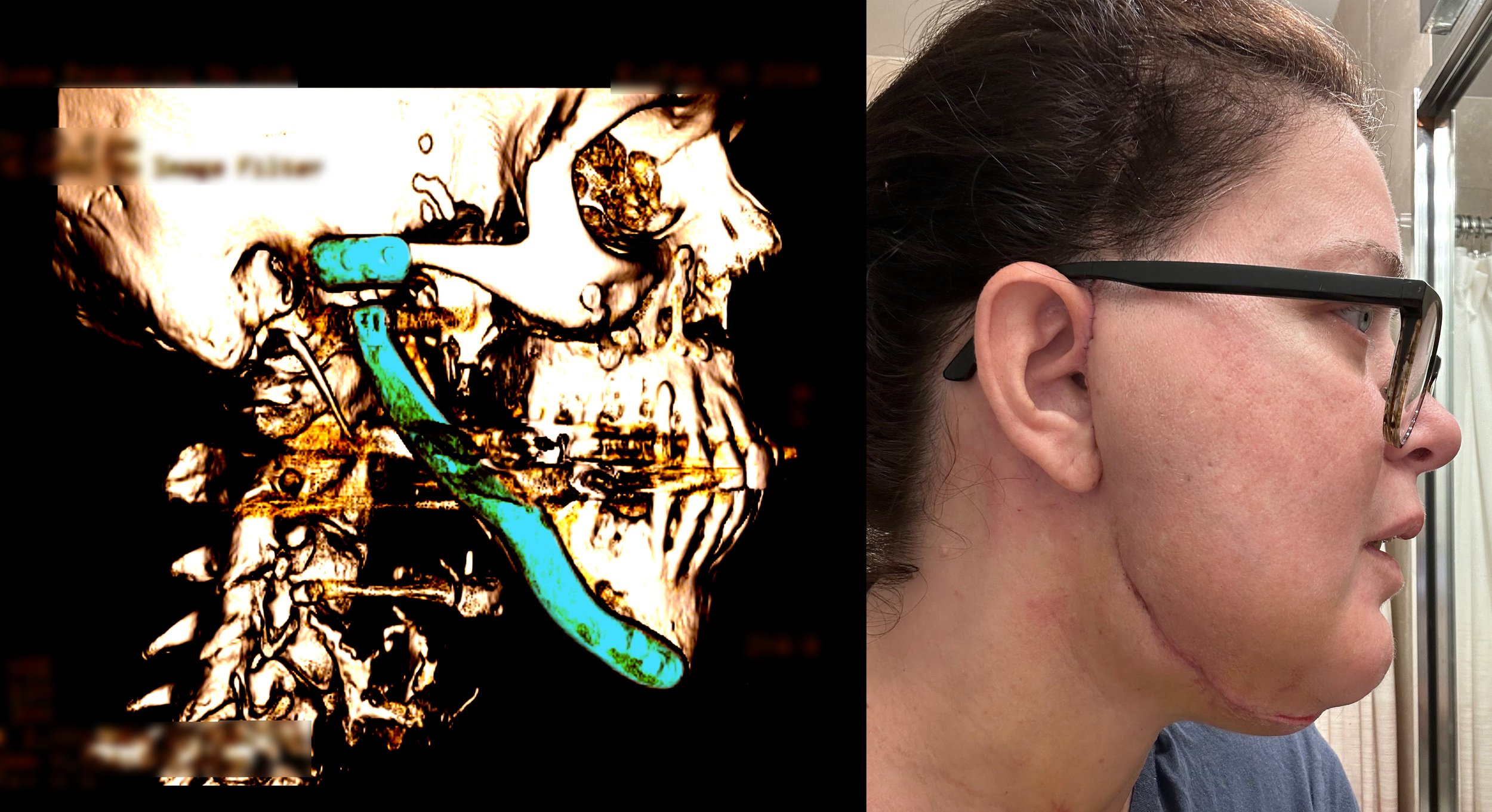
Schmidt, 52, of Poway, California, said she was diagnosed with TMJ disorder in 2000 due to headaches, and an orthodontist immediately recommended her for a splint, braces, and surgery.
After wearing the splint for only three days, Schmidt said, she was in “excruciating pain” and could no longer open her mouth far enough to eat solid food. Schmidt said she spent the next 17 years stuck on a “surgery carousel” with no escape, and eventually was in so much pain she abandoned her career as an aerospace scientist who worked alongside NASA astronauts.
Schmidt said her low point came in 2016. In an attempt to restore bone that had been cut away in prior surgeries, a surgeon implanted long screws into Schmidt’s jaw that protruded downward out of her neck. Schmidt said she was instructed to tighten those screws with a screwdriver daily for about 20 days, lengthening the corners of her jaw to restore the bone that had been lost. It didn’t work, Schmidt said, and she was left in more pain than ever.
“Every time you have a surgery, your pain gets worse,” Schmidt said. “If I could go back in time and go talk to younger Lisa, I would say ‘Run!’”
LISA SCHMIDT AND A 2017 MEDICAL SCAN OF HER FACE
Lack of Sufficient Evidence
Many of the shortcomings of TMJ care were laid bare in the 426-page report published by the national academies in March 2020 that received limited public attention amid the coronavirus pandemic. The report’s 18 authors include medical and dental experts from Harvard, Duke, Clemson, Michigan State, and Johns Hopkins universities.
Sean Mackey, a Stanford professor who co-led the team, said it found that patients were often steered toward costly treatments and “pathways of futility” instead of being taught to manage their pain through strategies and therapies with “good evidence.”
“We learned it’s a quagmire,” Mackey said. “There is a perverse incentive in our society that pays more for things we do to people than [for] talking and listening to people. … Some of those procedures, some of those surgeries, clearly are not helping people.”
Among its many findings, the national academies said it has been widely assumed in the field of dentistry that TMJ disorders are caused by a misaligned bite, so treatments have focused on patients’ teeth and bite for more than 50 years. But there is a “notable absence of sufficient evidence” that a misaligned bite is a cause of TMJ disorders, and the belief traces back to “inadequate research” in the 1960s that has been repeated in “poorly-designed studies” ever since, the report states.
Therefore, TMJ treatment that makes permanent changes to the bite — like installing braces or crowns or grinding teeth down — has “no supporting evidence,” according to the national academies report. The NIH warns that these TMJ treatments “don’t work and may make the problem worse.”
Dental splints, the most common TMJ treatment, also known as night guards or mouth guards, are removable dental appliances that are molded to fit over the teeth and can cost hundreds or even thousands of dollars out-of-pocket, according to the TMJ Association. Like most medical devices, splints generally go through the FDA’s 510(k) clearance process, which does not require each splint to be proven effective before it can be sold, according to the agency.
The national academies’ report states that splints produce “mixed results” for TMJ patients, and even when splints succeed at reducing jaw pain it is not understood why they work. Hundreds of splint designs exist, the report states, and some dentists reject research that challenges the use of splints unless it focuses on the specific design they prefer.
“Because of the hundreds of variations in [splint] design, it is unlikely that any study could ever be conducted that will be considered sufficient to a particular dentist with a pre-existing belief about the effectiveness of one appliance,” the report states.
Other treatments fare no better. The FDA has not labeled any drugs specifically for TMJ disorders, and pain medicines can be too weak or addictive to be a long-term solution, according to the TMJ Association. Botox injections may ease pain but have raised concerns about bone loss during animal testing. The NIH warns that minor surgeries that flush the jaw with liquid bring only temporary pain relief and that more complex surgeries should be reserved for severe cases because they have yet to be proved safe or effective in the long term.
To improve care, the national academies called for better education about TMJ disorders across medicine and dentistry and more research funding from the NIH, which has a “ripple effect” on research and training across the nation.
Since the 2020 report, the NIH has launched a TMJ research collaborative and increased annual research funding from about $15 million to about $34 million, D’Souza said. TMJ care was added to the standards that dental schools must teach to be accredited in 2022. The national academies launched an ongoing forum on TMJ disorders last year.
But TMJ funding still pales in comparison to other ailments. The NIH spends billions each year to research deadly diseases, like cancer and heart disease, that also afflict large numbers of Americans. It spends millions more on research of non-life-threatening conditions like arthritis, back pain, eczema, and headaches.
Mackey noted that much of the NIH’s spending is allocated by Congress.
“If Congress comes in and says, ‘We want to devote X amount of money to [TMJ],’ all of the sudden you will see an increase in money,” Mackey said. “So that’s my message to people out there: Raise your voices. Write your legislator.”
Total Jaw Replacement
Plagued by TMJ symptoms, and after failed treatments, some patients turn to a last resort: replacing their jaw joint with synthetic implants. Surgeons might replace the cartilage disk at the core of the joint or use “total joint replacement surgery” to fasten a metal hinge to the bones of the skull.
But the implants have a harrowing history: Several disk implants were recalled or discontinued in the ’90s due to dangerous failures. The FDA now classifies TMJ implants among its most closely monitored medical devices because the products on the market today can cause “adverse health consequences” if the devices fail, according to the agency’s website.
JENNY FELDMAN HAD 2 TOTAL JAW REPLACEMENTS
Two companies, Zimmer Biomet and Stryker, make the only total jaw replacement implants currently sold in the U.S.
Zimmer Biomet, which has made its implant for more than two decades, described it in email statements as “a safe and efficacious solution” for patients who need their jaw joint replaced, either due to TMJ disorders, failed surgeries, injuries, or other ailments. An FDA-mandated study completed in 2017 found about 14% of patients who get the Zimmer Biomet implant require additional surgery or removal within 10 years, said agency spokesperson Carly Pflaum.
Stryker, which in 2021 bought a company that made a total jaw replacement implant and now makes the implant itself, declined to comment. Although the NIH has advised TMJ patients to avoid surgery since at least 2022, Stryker launched a “patient-facing website” for the implant last year and is recruiting surgeons to be added to a “surgeon locator” feature on the site, according to posts on Facebook and LinkedIn.
A study of the Stryker implant’s success rate was mandated by the FDA and completed in 2020, but the agency has yet to make the results public.
D’Souza, the NIH official, said that based on her professional experience, she estimates that most total jaw replacement surgeries are ultimately ineffective.
“The success rate is low,” D’Souza said. “It is not very encouraging.”
Multiple patients provided KFF Health News and CBS News with medical records showing their total jaw replacement implants had to be removed due to malfunction, infection, or previously unknown metal allergies. Several patients said that since their implants were removed months or years ago, they have lived with no hinge in their jaw at all.
Kalinowski, the TMJ patient in Maine, has had portions of her jaw joint replaced six times, including receiving four implants. Her medical records show that the cartilage disk on her right side was replaced in 1986 with an implant that was later recalled and again in 1987 with another that was later discontinued. Her left and right disks were replaced in 1992 with a muscle flap and rib graft, respectively, and her entire right joint was replaced with yet another implant that was later discontinued in 1998. Both joints were replaced again in 2015, her records show.
Since then, Kalinowski said, her artificial jaw has functioned properly, although she remains in pain and cannot move her jaw from side to side. Her mouth hangs open when her face is at rest, and she drinks protein shakes for lunch because it’s easier than struggling with solid food.
But the “worst part,” Kalinowski said, is that her surgeries caused nerve damage on her lower face, and so she has not felt her husband’s kisses since the ’90s.
“If there was one moment in my life I could take back and do over again, it would be that first surgery. Because it set me on a trajectory,” Kalinowski said. “And it never goes away.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues.