Physical Therapy Coverage Often Ends When Patients Still Need It
/By Jordan Rau, KFF Health News
Mari Villar was slammed by a car that jumped the curb, breaking her legs and collapsing a lung. Amy Paulo was in pain from a femur surgery that wasn’t healing properly. Katie Kriegshauser suffered organ failure during pregnancy, weakening her so much that she couldn’t lift her baby daughter.
All went to physical therapy, but their health insurers stopped paying before any could walk without assistance. Paulo spent nearly $1,500 out of her own pocket for more sessions.
Millions of Americans rely on physical and occupational therapists to regain strength and motor skills after operations, diseases, and injuries. But recoveries are routinely stymied by a widespread constraint in health insurance policies: rigid caps on therapy sessions.
Insurers frequently limit such sessions to as few as 20 a year, a KFF Health News examination finds, even for people with severe damage such as spinal cord injuries and strokes, who may need months of treatment, multiple times a week. Patients can face a bind: Without therapy, they can’t return to work, but without working, they can’t afford the therapy.
Paulo said she pressed her insurer for more sessions, to no avail. “I said, ‘I’m in pain. I need the services. Is there anything I can do?’” she recalled. “They said, no, they can’t override the hard limit for the plan.”
A typical physical therapy session for a privately insured patient to improve daily functioning costs $192 on average, according to the Health Care Cost Institute. Most run from a half hour to an hour.
Insurers say annual visit limits help keep down costs, and therefore premiums, and are intended to prevent therapists from continuing treatment when patients are no longer improving. They say most injuries can be addressed in a dozen or fewer sessions and that people and employers who bought insurance could have purchased policies with better therapy benefits if it was a priority.
Atul Patel, a physiatrist in Overland Park, Kansas, and the treasurer of the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, said insurers’ desire to prevent gratuitous therapy is understandable but has “gone too far.”
“Most patients get way less therapy than they would actually benefit from,” he said.
Hard caps on rehab endure in part because of an omission in the Affordable Care Act. While that law required insurers to cover rehab and barred them from setting spending restrictions on a patient’s medical care, it did not prohibit establishing a maximum number of therapy sessions a year.
More than 29,000 ACA health plans — nearly 4 in 5 — limit the annual number of physical therapy sessions, according to a KFF Health News analysis of plans sold last year to individuals and small businesses. Caps generally ranged from 20 to 60 visits; the most common was 20 a year.
Health plans provided by employers often have limits of 20 or 30 sessions as well, said Cori Uccello, senior health fellow at the American Academy of Actuaries.
“It’s the gross reality in America right now,” said Sam Porritt, chairman of the Falling Forward Foundation, a Kansas-based philanthropy that has paid for therapy for about 200 patients who exhausted their insurance over the past decade. “No one knows about this except people in the industry. You find out about it when tragedy hits.”
Even in plans with no caps, patients are not guaranteed unlimited treatment. Therapists say insurers repeatedly require prior authorization, demanding a new request every two or three visits. Insurers frequently deny additional sessions if they believe there hasn’t been improvement.
“We’re seeing a lot of arbitrary denials just to see if you’ll appeal,” said Gwen Simons, a lawyer in Scarborough, Maine, who represents therapy practices. “That’s the point where the therapist throws up their hands.”
‘Couldn’t Pick Her Up’
Katie Kriegshauser, a 37-year-old psychologist from Kansas City, Missouri, developed pregnancy complications that shut down her liver, pancreas, and kidneys in November 2023.
After giving birth to her daughter, she spent more than three months in a hospital, undergoing multiple surgeries and losing more than 40 pounds so quickly that doctors suspected her nerves became damaged from compression. Her neurologist told her he doubted she would ever walk again.
Kriegshauser’s UnitedHealthcare insurance plan allowed 30 visits at Ability KC, a rehabilitation clinic in Kansas City. She burned through them in six weeks in 2024 because she needed both physical therapy, to regain her mobility, and occupational therapy, for daily tasks such as getting dressed.
“At that point I was starting to use the walker from being completely in the wheelchair,” Kriegshauser recalled. She said she wasn’t strong enough to change her daughter’s diaper. “I couldn’t pick her up out of her crib or put her down to sleep,” she said.
The Falling Forward Foundation paid for additional sessions that enabled her to walk independently and hold her daughter in her arms. “A huge amount of progress happened in that period after my insurance ran out,” she said.
In an unsigned statement, UnitedHealthcare said it covered the services that were included in Kriegshauser’s health plan. The company declined to permit an official to discuss its policies on the record because of security concerns.
A Shattered Teenager
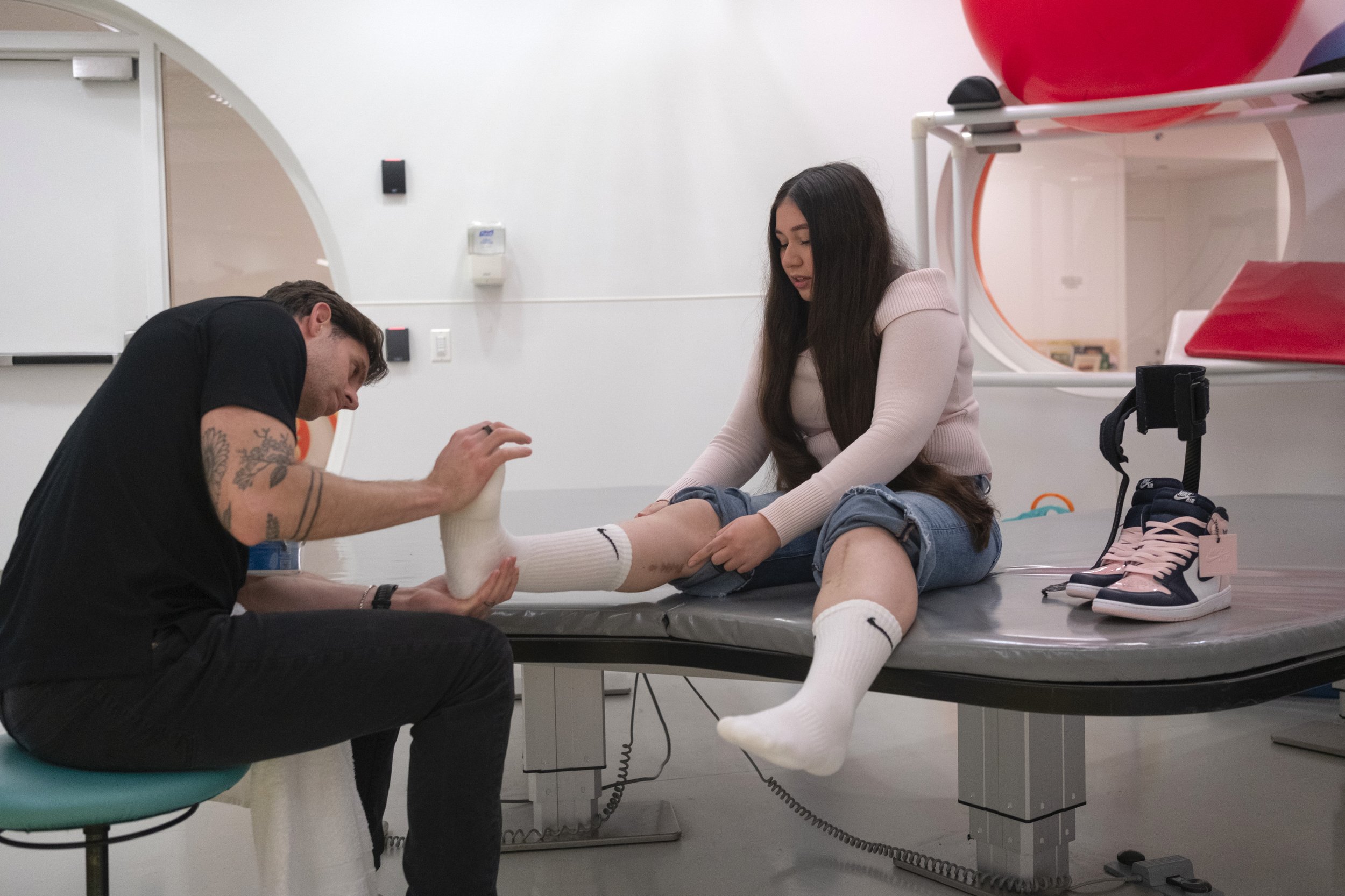
Patients who need therapy near the start of a health plan’s year are more likely to run out of visits. Mari Villar was 15 and had been walking with high school friends to get a bite to eat in May 2023 when a car leaped over a curb and smashed into her before the driver sped away.
The accident broke both her legs, lacerated her liver, damaged her colon, severed an artery in her right leg, and collapsed her lung. She has undergone 11 operations, including emergency exploratory surgery to stop internal bleeding, four angioplasties, and the installation of screws and plates to hold her leg bones together.
Villar spent nearly a month in Shirley Ryan AbilityLab’s hospital in Chicago. She was discharged after her mother’s insurer, Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Illinois, denied her physician’s request for five more days, making her more reliant on outpatient therapy, according to records shared by her mother, Megan Bracamontes.
Villar began going to one of Shirley Ryan’s outpatient clinics, but by the end of 2023, she had used up the 30 physical therapy and 30 occupational therapy visits the Blue Cross plan allowed.
Because the plan ran from July to June, she had no sessions left for the first half of 2024.
MARI VILLAR AND HER THERAPIST
“I couldn't do much,” Villar said. “I made lots of progress there, but I was still on crutches.”
Dave Van de Walle, a Blue Cross spokesperson, said in an email that the insurer does not comment on individual cases. Razia Hashmi, vice president for clinical affairs at the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association, said in a written statement that patients who have run out of sessions should “explore alternative treatment plans” including home exercises.
Villar received some extra sessions from the Falling Forward Foundation. While her plan year has reset, Villar is postponing most therapy sessions until after her next surgery so she will be less likely to run out again. Bracamontes said her daughter still can’t feel or move her right foot and needs three more operations: one to relieve nerve pain, and two to try to restore mobility in her foot by lengthening her Achilles tendon and transferring a tendon in her left leg into her right.
“Therapy caps are very unfair because everyone’s situation is different,” Villar said. “I really depend on my sessions to get me to a new normalcy. And not having that and going through all these procedures is scary to think about.”
Rationing Therapy
Most people who use all their sessions either stop going or pay out-of-pocket for extra therapy.
Amy Paulo, a 34-year-old Massachusetts woman recovering from two operations on her left leg, maxed out the 40 visits covered by Blue Cross Blue Shield of Massachusetts in 2024, so she spent $1,445 out-of-pocket for 17 therapy sessions.
Paulo needed physical therapy to recover from several surgeries to shorten her left leg to the length of her right leg — the difference a consequence of juvenile arthritis. Her recovery was prolonged, she said, because her femur didn’t heal properly after one of the operations, in which surgeons cut out the middle of her femur and put a rod in its place.
“I went ballistic on Blue Cross many, many times,” said Paulo, who works with developmentally delayed children.”
Amy McHugh, a Blue Cross spokesperson, declined to discuss Paulo’s case. In an email, she said most employers who hire Blue Cross to administer their health benefits choose plans with “our standard” 60-visit limit, which she said is more generous than most insurers offer, but some employers “choose to allow for more or fewer visits per year.”
Paulo said she expects to restrict her therapy sessions to once a week instead of the recommended twice a week because she’ll need more help after an upcoming operation on her leg.
“We had to plan to save my visits for this surgery, as ridiculous as it sounds,” she said.
Medicare Is More Generous
People with commercial insurance plans face more hurdles than those on Medicare, which sets dollar thresholds on therapy each year but allows therapists to continue providing services if they document medical necessity. This year the limits are $2,410 for physical and speech therapy and $2,410 for occupational therapy.
Private Medicare Advantage plans don’t have visit or dollar caps, but they often require prior authorization every few visits. The U.S. Senate Permanent Subcommittee on Investigations found last year that MA plans deny requests for physical and occupational therapy at hospitals and nursing homes at higher rates than they reject other medical services.
Therapists say many commercial plans require prior authorization and mete out approvals parsimoniously. Insurers often make therapists submit detailed notes, sometimes for each session, documenting patients’ treatment plans, goals, and test results showing how well they perform each exercise.
“It’s a battle of getting visits,” said Jackee Ndwaru, an occupational therapist in Jacksonville, Florida. “If you can’t show progress they’re not going to approve.”
An Insurer Overruled
Marjorie Haney’s insurance plan covered 20 therapy sessions a year, but Anthem Blue Cross Blue Shield approved only a few visits at a time for the rotator cuff she tore in a bike accident in Maine. After 13 visits in 2021, Anthem refused to approve more, writing that her medical records “do not show you made progress with specific daily tasks,” according to the denial letter.
Haney, a physical therapist herself, said the decision made no sense because at that stage of her recovery, the therapy was focused on preventing her shoulder from freezing up and gradually expanding its range of motion.
“I went through those visits like they were water,” Haney, now 57, said. “My range was getting better, but functionally I couldn’t use my arm to lift things.”
Haney appealed to Maine’s insurance bureau for an independent review. In its report overturning Anthem’s decision, the bureau’s physician consultant, William Barreto, concluded that Haney had made “substantial improvement” — she no longer needed a shoulder sling and was able to return to work with restrictions. Barreto also noted that nothing in Anthem’s policy required progress with specific daily tasks, which was the basis for Anthem’s refusal.
“Given the member’s substantial restriction in active range of motion and inability to begin strengthening exercises, there is remaining deficit that requires the skills and training of a qualified physical therapist,” the report said.
Anthem said it requires repeated assessments before authorizing additional visits “to ensure the member is receiving the right care for the right period of time based on his or her care needs.” In the statement provided by Stephanie DuBois, an Anthem spokesperson, the insurer said this process “also helps prevent members from using up all their covered treatment benefits too quickly, especially if they don’t end up needing the maximum number of therapy visits.”
In 2023, Maine passed a law banning prior authorization for the first 12 rehab visits, making it one of the few states to curb insurer limitations on physical therapy. The law doesn’t protect residents with plans based in other states or plans from a Maine employer who self-insures.
Haney said after she won her appeal, she spaced out the sessions her plan permitted by going once weekly. “I got another month,” she said, “and I stretched it out to six weeks.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues.