Don’t Let Them Stop the Stem Cell Movement
/By A. Rahman Ford, Columnist
Somewhat lost in Donald Trump’s presidential victory was the resounding statement made by voters that medical marijuana is here to stay. Those people-driven victories were monumental for millions suffering from painful and debilitating illnesses -- people who could achieve a life-saving benefit from marijuana or its derivatives.
It’s only a matter of time before the DEA changes its ridiculous classification of marijuana as a Schedule I controlled substance.
I believe that one of the next challenges in the wellness movement is the FDA’s control over your own stem cells, or as I call them, personal stem cells. Quite frankly, the DEA’s position on marijuana is about as misplaced as the FDA’s position on you using the cells God gave you to heal yourself.
Some scientists have been pushing quite a bit of manufactured controversy around the issue. Those same scientists tried the same thing with marijuana. But now the people know the truth.
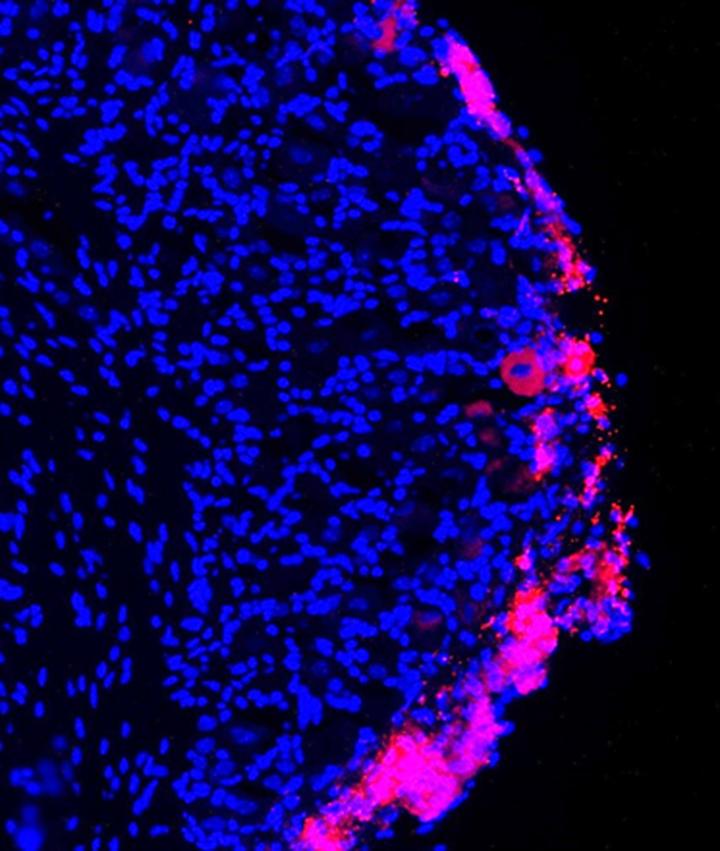
Personal stem cells are simple to understand. I’m not talking about embryos, umbilical cords or artificial cells grown by some scientist in a lab. When I talk about personal stem cells, I’m talking about master cells cultivated from your own bone marrow or fat.
Yes, you have stem cells in your own body that can heal you.
In marijuana terms, it’s like you’re your own stem cell “grow house.” Your own cells can be used to heal any number of physical ailments, including orthopedic issues. Orthopedists have been using the procedure for years, and there is also evidence that stem cells can be used to heal autoimmune diseases.
Like marijuana, we really have no idea how many ailments can be improved or even cured with personal stem cells.
If you’re wondering whether personal stem cells can actually heal, look no further than professional sports. Recently, Bartolo Colon, currently the oldest major league baseball player at 43 years of age, signed a $12.5 million pitching contract with the Atlanta Braves. How in the world is he able to be so productive at an age where most players are long retired? You guessed it – his own stem cells.
What about NFL Hall of Famer and two-time Super Bowl winner Peyton Manning, who literally broke his neck playing the game he loved? Yes, his own stem cells. International athletes like tennis champion Rafael Nadal have benefitted as well. In fact, hundreds of professional athletes have healed from serious injuries by using their own stem cells.
Personal stem cells can work.
Unfortunately, many athletes have to go overseas to use their own God-given healing potential, because the FDA doesn’t allow certain techniques to expand your really strong (mesenchymal) stem cells. But these wealthy, well-connected athletes who earn their living by being fit -- often enduring severe injuries and pain -- know the truth. Your own stem cells can heal you.
Just think how many wounded combat veterans could benefit from their own cells! A 2014 University of Michigan study found that 60 percent of U.S. Army soldiers who were unable to return to a military career after an Iraq deployment couldn’t do so because of a muscle, bone or joint injury. The strongest predictors of inability to serve were fractures and chronic knee, shoulder, spine and back pain.
But it’s not just musculoskeletal conditions. Our troops also have crippling brain injuries from IED and other bomb blasts. According to the Pittsburgh Tribune Review, tens of thousands of combat veterans returning from Iraq and Afghanistan with undiagnosed brain injuries “often were ‘thrown into a canyon’ – falling deeper into despair and sometimes flirting with suicide or addiction.”
It gets worse. To cope with the pain and depression of injury, many wounded warriors turn to addictive pharmaceutical painkillers or illegal street drugs. A 2011 American Public Health Association report found that the overdose rate for veterans on opioid painkillers was twice the national average, and that they are more likely to become addicted to heroin.
Opioid abuse is such an epidemic that, in a recent letter to physicians, the Surgeon General called it a crisis and launched the “Turn the Tide” campaign to raise awareness about the issue.
Fortunately, many wounded warriors have already begun turning the tide by replacing their toxic pills with medical marijuana. Now, we owe it to our troops to help them turn the tide even further, by giving them another option – personal stem cells.
We celebrate our troops with parades and salutes on Veteran’s Day, Memorial Day and during just about every major sporting event, and justifiably so. But maybe the best way to celebrate them is to allow them to heal themselves with their own cells so that they can once again be the parents, siblings and children we love. Our government has a moral and ethical obligation to do so, and we the people have an ethical and moral obligation to make them do it.
Stem Cell Therapy Not FDA Approved
I want to be clear: clinical use of adult, embryonic and umbilical cord stem cells are not FDA approved, and any determination as to their safety or efficacy requires further research (although, in the interest of full disclosure, I have had umbilical cord stem cells in China and the therapy helped me greatly with no negative effects). These stem cells are properly under the domain of the FDA because they are biological agents that are taken from one person and injected into another person and intended to treat a disease.
What I’m talking about are cells that go from YOU into YOU. Personal stem cells are as natural as marijuana, and the federal government should acknowledge that your use of your own cells should be a transaction between you and a licensed physician, and regulated at the state level.
States like Colorado and Washington have already proven how safe and healing – not to mention lucrative – marijuana can be, despite what all of the “experts” were saying. Your own stem cells are no different.
Right now, personal stem cells are technically legal, but the future regulatory landscape is so uncertain that few physicians offer it and few Americans can afford it. Rather than expanding access to personal stem cells, the FDA has recently tried to restrict their use.
The proposed action by the FDA is wrong. Unfortunately, it seems like the agency is refusing to hear the cries of persons with disabilities (like myself) and wounded warriors who come home crippled after serving abroad -- so that the children of federal agency bureaucrats can be safe here at home.
I believe marijuana legalization gives personal stem cell advocates hope. The legalization movement succeeded despite federal intransigence because of the success of direct democracy. People voted at the state level in referendums, without elected officials operating as self-interested intermediaries.
Given the important nature of this issue, and the apparent ineffectiveness of federal government lobbying and litigation alone, the personal stem cell movement may need to add a referendum component as well. It may be difficult, but it can be done.
Educate yourself, and then educate others. Human beings are not drugs. We need to keep it that way.
A. Rahman Ford, PhD, is a lawyer and research professional. He is a graduate of Rutgers University and the Howard University School of Law, where he served as Editor in Chief of the Howard Law Journal. He earned his PhD at the University of Pennsylvania.
Dr. Ford is not affiliated with any stem cell treatment provider. He suffers from chronic inflammation in his digestive tract and is unable to eat solid food.
Pain News Network invites other readers to share their stories with us. Send them to: editor@PainNewsNetwork.org.
The information in this column should not be considered as professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. It is for informational purposes only and represent the author’s opinions alone. It does not inherently express or reflect the views, opinions and/or positions of Pain News Network.